Description
The best known of its effects is the regulation of sleep rhythms. It promotes overall sleep duration, sleep quality and faster falling asleep. It also helps to regulate shifted sleep time “jet lag”.
Information
Dosage: 1 capsule daily (approximately one hour before bedtime) with plenty of water
Recommended dosage: 1 capsule
Ingredients: L-glutamine, vegetarian capsule (hydroxypropylmethylcellulose), melatonin
Storage: store in a dry place, out of direct sunlight at temperatures between 6-25°C. Do not expose to frost or moisture.
Warning: the product is not suitable for children, persons under 18 years of age, pregnant and lactating women. The food supplement must not be used as a substitute for a varied diet. Keep out of reach of small children. The established recommended daily dose must not be exceeded.
Consumption: As indicated on the packaging.
Most of us know melatonin by the name of the sleep hormone. In this article, we would like to introduce you to its functions in our body and its impact on immunity and our overall health.
Melatonin is a hormone released in the brain that helps with the timing of our internal clocks, i.e. sleep and wakefulness. In newborn babies, melatonin starts to be released as early as the third month. Throughout life, the times of the highest intensity of melatonin released change, resulting in different times natural to us for sleeping and waking. Some people have been found to produce significantly less melatonin than others during their lifetime, which may have implications for faster aging, general deterioration in cognitive, psychological and social function, and sleep disturbances. The amount of melatonin secreted also correlates with daily and seasonal changes in our immune system, proving that it plays an important role in regulating immunity.
What is immunity and how does it work?
If our immunity works properly, the body can defend itself against pathogens and thus prevent various diseases. The immune system is an essential mechanism for maintaining homeostasis, a state of normal body function where it is not disturbed by any changes from the external environment. The immune system is made up of various cells, molecules and lymphoid organs. These are mainly white blood cells, specific antigen receptors on the surface of T and B cells, the thymus and the bone marrow where these cells are formed.
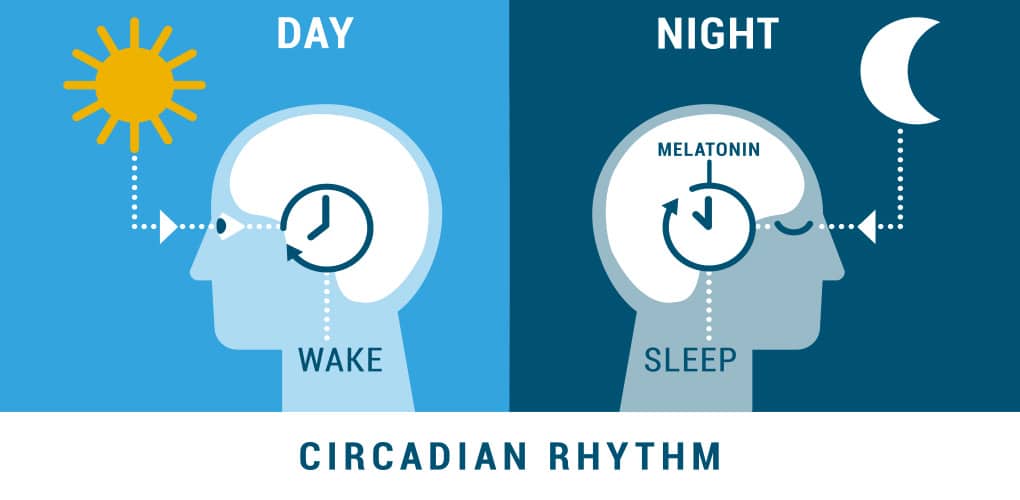
Living organisms use a natural circadian clock (circadian rhythm) to achieve homeostasis. These help the body to prepare for the change of light and darkness, i.e. they work on the basis of the alternation of day and night. When these rhythms are in tune with external changes, our organs function better, we are in a better mood and our immune system is more resistant to various diseases.
How is melatonin related?
When a beam of light hits the retina of our eye, the nerves carry this information to the brain. The pineal gland secretes a small amount of melatonin based on this information, which latches onto its receptors in the suprachiasmatic nucleus. There it prevents its further production. In the dark, however, melatonin is secreted in large quantities because it is not blocked by anything.
Due to the abundant distribution of its receptors throughout the body, it influences many functions in the body. It boosts the immune system, positively influences the development of reproductive organs, improves fertility, affects memory and learning, and also has antioxidant effects.
Studies have shown that melatonin supplements can alleviate jet lag symptoms on long-haul flights. It is also recommended for patients with delayed sleep-wake phase disorder, for some sleep problems in children, or for anxiety before and after surgery (1).
Blind patients and melatonin
Persons who are totally blind often experience a disruption of the 24-hour sleep cycle. Because they cannot naturally receive light signals important to the natural circadian rhythm, their body follows a 24-hour cycle, but the sleep clock is constantly shifting. These persons are unable to correct their circadian rhythm naturally on their own, as would be possible for sighted people. The natural production of melatonin in this condition may be too low, or conversely too high, both of which can lead to problems. It is the hormone melatonin administered as part of the treatment that has been shown to be effective in blind patients. In sighted patients suffering from the same disorder, melatonin is also used in treatment, but usually not as the only treatment.
Sources:
https://zdravoteka.sk/magazin/cirkadianny-rytmus-poruchy-spanku-16-potravin-pomozu-zaspat/
https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/non-24-hour-sleep-wake-disorder/
(1) https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/melatonin-what-you-need-to-know